SEC believes Artificial Intelligence (AI) to be a key IoT technology and is engaged in its research and development.
From robotics fields including the development of platforms that “link” robot development and AI, and making circuitization of intelligent processing in robots, to machine learning-based failure detection and prediction in spacecraft, SEC is pursuing the possibilities of AI in unique fields.
We are also engaging in initiatives to establish a new style of development in relation to generative AI technology.
We are collaborating with Kyushu Institute of Technology and other organizations to develop and implement ultra-low-power edge AI chips and to build a software development environment for use with these chips.
AI has become an essential technology for progress in society, but it still presents many challenges in terms of processing power, energy efficiency, and other areas. To tackle these issues, it is essential to take the latest insight from neuroscience and neurophysiology, as well as the computer theory that can put this insight into practice, and to integrate these concepts into hardware research.
We are working to develop an edge AI chip with an integrated circuit that can run models based on reservoir computing—a type of machine learning algorithm that expresses the mechanisms of the human brain as formulas. We also seek to utilize these chips and realize real-world implementation with AI-powered edge devices in the fields of robotics and IoT. At the same time, we are engaging in initiatives to build a software development environment to achieve our goal of implementation.
SEC is conducting research into the circuitization of intelligent processing—that is, ensuring that intelligent processing circuits incorporate field-programmable gate arrays (FPGA)—and into turning this circuitized intelligent processing into a platform that can be manipulated as a component of RT-Middleware. This research is being conducted jointly with Hakaru Tamukoh, associate professor at the Department of Brain Science and Engineering, Graduate School of Life Science and Systems Engineering, Kyushu Institute of Technology.
Development of existing AI technologies has primarily been driven by information processing. For this reason, AI implementation is premised on large-scale computing resources, including CPUs and memory. However, this dependence on large-scale hardware is a significant obstacle if we wish to apply AI to service robots. More specifically, there is a need to ensure that the platforms on which AI operate consume less power, generate less heat, and are more compact, while retaining the current high-speed processing functions of AI. One practical method for realizing this is the integration of field programmable gate arrays into intelligent processing circuits. If we are able to turn this circuitized intelligent processing into a platform that can be manipulated as a component of RT-Middleware, it will not only facilitate the application of robot AI, but also lead to progress in the integration of AI and robots. As a result, our research seeks both to circuitize intelligent processing and subsequently apply it to robot platforms.
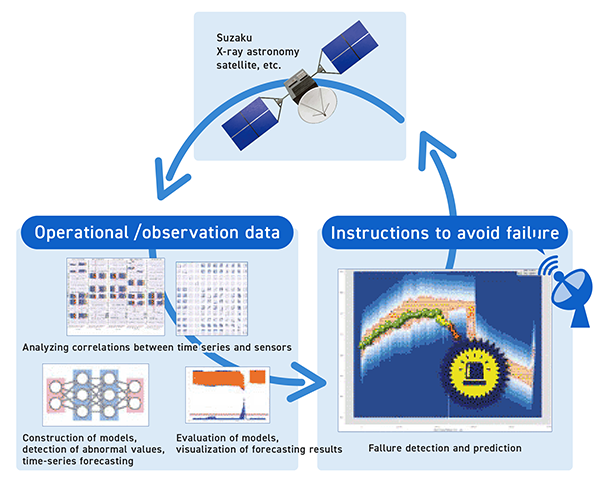
Together with the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), SEC is researching the use of AI to analyze spacecraft operational data and implement failure analysis in spacecraft.
Failure analysis is a major field for AI applications, and the implementation of AI-based failure analysis in various machines is advancing. The goal of our research is to apply AI-based failure analysis to spacecraft, and thereby contribute to the safety of space exploration. High levels of safety and reliability are required of spacecraft, and operational environments in which danger can be predicted and accidents avoided are desirable. Our research seeks to contribute to stable spacecraft operation by using AI to analyze spacecraft operational data, carry out failure analysis, and accumulate technologies capable of detecting spacecraft failures in advance.
At SEC we are researching AI and machine learning platforms that can be easily used and shared by robot researchers and AI researchers alike, with the goal of integrating robot development and AI development. This research is taking place jointly with Tetsuya Ogata, Professor, Department of Intermedia Art and Science, School of Fundamental Science and Engineering, Waseda University.
For service robots to be of use, they must possess high-level AI. To make software development for service robots more efficient, robot parts are first being componentized then assembled. Development platforms such as RT-Middleware and the Robot Operating System exist, but they are not general-purpose platforms that are accessible to everyone. Robotics is a practical field in which AI can be applied to real world-situations and, as such, going forward we can expect greater integration between AI and robots. We are therefore engaged in the research and development of integrated development environments that can be easily used both by robot researchers and AI researchers.